What Is a DEX? A Comprehensive Guide to Decentralized Exchanges
TL;DR
- Decentralized exchanges offer enhanced privacy, security, and user control over assets, removing the need for intermediaries found in centralized exchanges.
- Challenges like fragmented liquidity, user interface complexity, and high gas fees remain, but innovations in scalability, market-making mechanisms, and aggregation are steadily improving DEX efficiency.
- Cross-chain swaps and DEX aggregators are key technologies driving the future of decentralized trading, enabling users to trade across multiple blockchains while optimizing liquidity and rates.
In recent years, centralized cryptocurrency exchanges (CEXs) have struggled to maintain user trust as customers become increasingly aware of the risks of CEXs managing their funds.
The 2022 collapse of FTX, Kucoin’s ‘criminal conspiracy’ charges, and the founder of Binance serving a jail sentence for money laundering have done little to inspire confidence in the industry. These high-profile incidents highlight an urgent need for a more secure, transparent alternative in crypto trading—one that decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are increasingly positioned to offer.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take a closer look at DEXs—how they work, why they matter, their types, and their pros and cons. Whether you’re a crypto veteran or just dipping your toes into the digital asset pool, understanding DEXs is essential for navigating the exciting and turbulent waters of the crypto market.
What Is a DEX (Decentralized Exchange)?
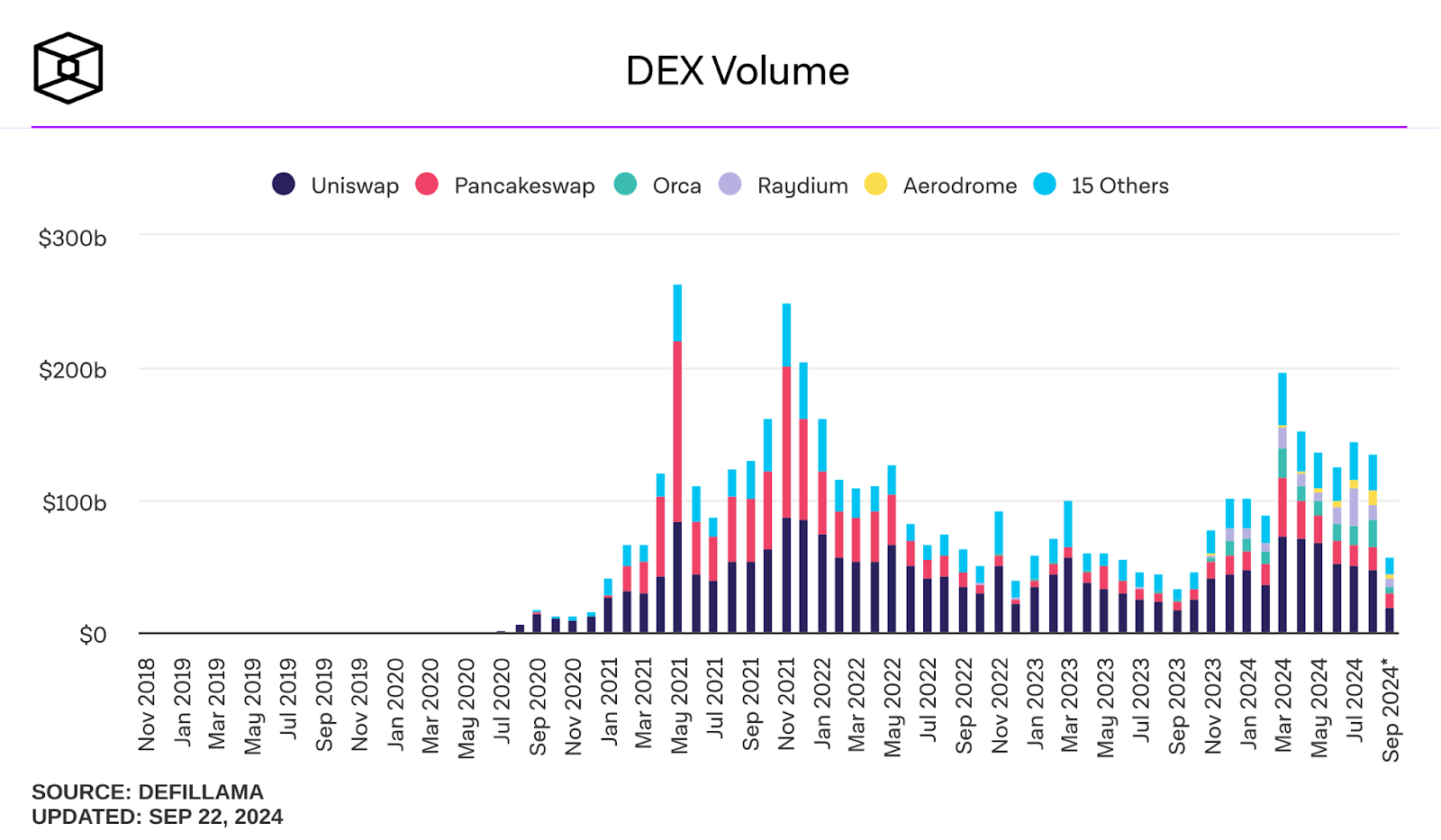
The chart includes the spot volume of DEXs. All volume is filtered for flash trades, in which a trader takes out a large loan to execute a high-volume trade and then quickly pays it back.
Source: The Block Data
A DEX is an application built on blockchain technology that allows peer-to-peer crypto transactions without relying on a centralized financial authority.
At its core, DEXs are non-custodial and designed to eliminate the need for intermediaries, meaning you keep full ownership and control of your assets throughout the trading process. This adds a layer of security, reducing the risks associated with centralized exchanges, such as hacks or shutdowns.
Transparency is another defining feature—every transaction is recorded on the blockchain, creating a public, immutable record. DEXs also tend to offer a wider variety of trading pairs, including newer tokens that may not be available on centralized exchanges. Since no central authority decides which assets to support, users often find a more diverse selection of cryptocurrencies to trade.
Distinguishing Between DEX and CEX (Centralized Exchanges)
The choice between using DEX or CEX platforms often comes down to individual preferences, trading needs, and comfort with technology. Here are the key differences:
- Control of Funds: On a DEX crypto exchange, users retain control of their private keys and, consequently, their funds. In contrast, when using a CEX, you must deposit your assets into the exchange’s wallet.
- Order Matching: DEXs rely on smart contracts to match and execute trades automatically, while CEXs use a centralized order book managed by the exchange.
- KYC Requirements: Most DEXs don’t require KYC (Know Your Customer) checks, giving you more privacy. CEXs often require KYC to meet regulatory requirements, which means sharing personal information.
- Speed and Liquidity: CEXs usually have faster trade execution and higher liquidity, thanks to their centralized setup. DEXs are improving but can still lag in these areas, especially during high demand.
- User Interface: CEXs typically offer a more user-friendly experience if you’re newer to crypto. DEXs can be a bit more complex, requiring a deeper understanding of blockchain networks and wallet management.
- Security: DEXs spread the risk by being decentralized, making them less prone to major security breaches or single points of failure. In contrast, CEXs, being centralized, can be more vulnerable to hacks or internal mismanagement.
Understanding these differences is key for anyone diving into crypto trading. While CEXs have been the go-to for most traders due to their ease of use, DEXs are quickly gaining ground by offering more control, transparency, and a decentralized trading experience.
Take, for instance, the experience of many early traders who began looking for alternatives that gave them more control after dealing with exchange hacks or sudden withdrawal freezes on centralized platforms. It’s a shift that’s hard to ignore, especially if you’re serious about fully owning your crypto.
How Does a DEX Work?
DEX crypto exchanges operate on a fundamentally different model than traditional exchanges, leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts to facilitate peer-to-peer (P2P) trading.
Here’s a breakdown of how the blockchain technology behind DEX works:
- Distributed Network: Instead of relying on a central server, DEXs run on a global network of computers (nodes) spread across different locations.
- Consensus Mechanisms: These networks use various consensus algorithms to validate and confirm transactions, ensuring all nodes agree without a central authority.
- Transparency: Every transaction is recorded on the blockchain, creating a public and verifiable history of trades for anyone to see.
- Security Model: The decentralized nature of blockchain makes it highly resistant to manipulation, adding an extra layer of security against attacks or tampering.
The 4 Different Types of DEXs
As the decentralized exchange ecosystem has evolved, several distinct models have emerged, each with its unique characteristics and advantages. Understanding these different types of DEXs is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the world of decentralized trading. Let’s explore the four main types of DEXs:
Order Book Models: On-Chain vs Off-Chain
Order book DEXs mimic traditional exchanges by maintaining a list of buy and sell orders:
- On-Chain Order Books: All orders are stored and matched on the blockchain. This provides maximum transparency but can be slow and expensive due to network fees.
- Off-Chain Order Books: Orders are stored off-chain and only settled on the blockchain. This approach offers faster trading but sacrifices some decentralization.
- Hybrid Models: Some DEXs combine on-chain and off-chain processes to balance speed and decentralization.
Some popular order book DEXs include 0x, dYdX, Polkadex, Carbon DeFi, and Loopring DEX. While these platforms can offer more advanced trading features, they may also struggle with liquidity on less popular trading pairs.
Automated Market Maker (AMM) Models
AMMs have become increasingly popular in the DEX space due to their innovative approach:
- Liquidity Pools: Users provide liquidity by depositing pairs of tokens into pools.
- Algorithmic Pricing: Prices are determined by a mathematical formula based on the ratio of tokens in the pool.
- Constant Product Formula: Many AMMs use this formula (x * y = k) to maintain a constant balance between assets.
- Passive Market Making: Liquidity providers earn fees without actively managing their positions.
AMM DEXs require market makers to lock funds into smart contracts, which can pose a higher security risk due to large amounts of pooled funds. This vulnerability came to light following the 2022 Axie Infinity Ronin bridge hack, where $650 million was stolen.
Most AMMs are primarily designed to facilitate cryptocurrency swaps but can also be used for trading NFTs, tokenized real-world assets, and carbon credits. Popular AMM DEXs include Uniswap, Pendle, Aerodrome Finance, Balancer, PancakeSwap, Osmosis, Raydium, and Curve.
While AMMs have addressed many liquidity challenges that other DEX models face, they come with risks like impermanent loss for liquidity providers and slippage on larger trades, especially during market volatility. Platforms like IDEX have introduced a hybrid approach to offer the best of AMM and order book models.
DEX Aggregator Models
DEX aggregators are a newer development in the ecosystem, designed to optimize trading across multiple DEXs:
- Multi-DEX Routing: Aggregators search for the best prices across various DEXs, even across different blockchains, and split orders to secure the best overall deal.
- Improved Liquidity: By accessing liquidity from multiple sources, including cross-chain pools, aggregators can offer better liquidity than individual DEXs, ensuring smoother trades.
- Cross-Chain Swaps: Many aggregators facilitate cross-chain swaps, allowing users to seamlessly trade assets across blockchains and opening up new trading opportunities without needing multiple platforms. Some use advanced algorithms to minimize gas fees, even when executing complex, multi-step transactions across different blockchains.
- User-Friendly Interface: Aggregators typically provide a simple, intuitive interface that hides the complexity of interacting with multiple DEXs and blockchains, making it easier for traders to take advantage of cross-chain and multi-DEX strategies.
Instead of manually working out the best price for a trade, users can use DEX aggregators to work out the hard part and profit from the price difference. 1inch, Open Ocean, and Rubic are popular DEX aggregators enabling crypto traders to find the best deal for the token pair they want to trade.
What Are the Benefits of Using a DEX?
DEXs have been a true zero-to-one innovation, revolutionizing user autonomy, transparency, and security in crypto. Let’s dive into the key benefits that make DEX crypto so appealing to cryptocurrency traders and enthusiasts alike.
- Anonymity and Privacy: One of the most attractive features of DEX platforms is their enhanced privacy. Most DEXs don’t require KYC procedures, allowing users to trade anonymously. Trades happen directly between wallets, minimizing your activity’s digital footprint, and since DEXs don’t store personal information, the risk of data breaches is significantly reduced.
- No Middleman, “Not your keys, not your coins”: Decentralized trading removes the need for intermediaries, offering several security advantages like letting users control their assets, executing trades through trustless smart contracts, and cutting down on counterparty risk. This combination helps shield against fraud and hacking, a massive win in crypto. Fees are also often lower since there’s no central authority taking a cut. Additionally, DEXs provide censorship resistance, meaning no single entity can block access or stop you from trading. Lastly, the transparency of blockchain ensures that every transaction is publicly recorded, creating a permanent and unalterable history of activity.
- Tapping into Unlisted Tokens and Assets: DEX crypto exchanges can list almost any token compatible with their blockchain, providing access to a broader range of cryptocurrencies. Traders often get early access to new or niche tokens on DEXs before they hit centralized platforms. DEXs also support long-tail assets, offering markets for less popular tokens that CEXs might overlook. Plus, anyone can create trading pairs with permissionless listing, encouraging innovation and expanding diversity within the crypto ecosystem.
While these benefits make DEXs an attractive option, users still need to stay sharp—smart contract vulnerabilities and the wild swings of market volatility are very real risks. As with any financial technology, being aware of these risks can help you make more informed decisions and navigate the DEX landscape more safely.
Risks and Challenges of Using a DEX
Despite the advantages DEXs bring, they are not without their challenges and security concerns:
- Navigating Complex User Interfaces: Newcomers to DEXs often face challenges due to the complexity of their interfaces, which require a deeper understanding of blockchain and crypto trading. Wallet integration and concepts like gas fees can be confusing for those used to centralized exchanges. With minimal customer support, users are left to troubleshoot on their own. Starting with small transactions and gradually exploring the platform can help ease the learning curve.
- Issues With Liquidity and Slippage: Liquidity and slippage are common concerns in decentralized trading, particularly on smaller or niche platforms with lower trading volumes. This can lead to price slippage, where large trades impact execution prices. Liquidity providers also face the risk of impermanent loss when token prices fluctuate. Consider using DEX aggregators or splitting large trades into smaller ones to reduce slippage.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Smart contract risks include reentrancy attacks, overflow errors, and front-running, as seen in Uniswap’s 2023 sandwich attack that resulted in a $25.2 million loss. Code exploits, where malicious actors find flaws in the contract code, can lead to significant fund losses. Oracle manipulation is another concern, as inaccurate data can skew outcomes. Even well-designed protocols can suffer from poor implementation or liquidity issues. To minimize exposure, it’s best to use well-established DEXs with a proven security track record that undergo regular contract audits.
- Riskier Tokens: The open nature of DEXs exposes users to riskier assets, as token listings are often not thoroughly vetted. This can lead to scam tokens or pump-and-dump schemes that manipulate prices in low-liquidity markets. Some tokens may also face regulatory issues, adding legal risks for traders. Researching tokens thoroughly before trading is essential to avoid these pitfalls.
Decentralized exchanges are still relatively new, and they are constantly being targeted by hackers. Many reputable DEX crypto exchanges employ advanced security measures, including two-factor authentication (2FA), cold storage, and encryption protocols. These features protect your assets from potential threats and provide peace of mind.
The best decentralized exchanges should have high trading volumes and active users. This ensures that you can buy or sell assets without significant price fluctuations. Additionally, look for DEXs that offer 24/7 customer service through various channels like live chat, email, or phone. It’s also best to research reviews and testimonials to gauge the experiences of other users.
How to Use a DEX for Trading: Step-by-Step Guide
Trading on a decentralized exchange involves a few essential steps that differ from traditional centralized platforms. Here’s a quick guide to help you get started:
- Create a Wallet: Unlike centralized exchanges, DEXs don’t require an account—you manage everything through your wallet. Ensure the wallet supports the blockchain your DEX operates on, such as Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain. Some wallets offer built-in DEX functionality, such as Rubic’s Metamask Snap, making trading more seamless.
- Connect Your Wallet: Go to the DEX website and select the “Connect Wallet” option. Approve the connection through your wallet. Make sure your wallet is set to the right blockchain network. If using a browser extension wallet, connect it to your web browser.
- Start Trading: With your wallet connected, you can immediately begin trading. Select the cryptocurrencies you want to trade (e.g., ETH to TOKEN-A). Specify how much you want to buy or sell. The DEX will display estimated outputs based on liquidity and pricing. Check all the transaction details, including fees and slippage tolerance. Make adjustments if needed. Click “Swap” or “Trade” to initiate the transaction, then confirm the trade in your wallet. Once the blockchain confirms the transaction, it will execute. Depending on network conditions, this process could take a few seconds to minutes. After confirmation, check your wallet to ensure the traded tokens have arrived.
Understanding DEX Crypto Exchange Fees
There are plenty of decentralized exchanges out there, catering to different risk appetites and trading styles—each offering perks like cheaper rates, lower transaction fees, or faster settlement times. What often sets these DEXs apart is their gas fees and exchange rates, which can significantly affect the cost-efficiency of your trades.
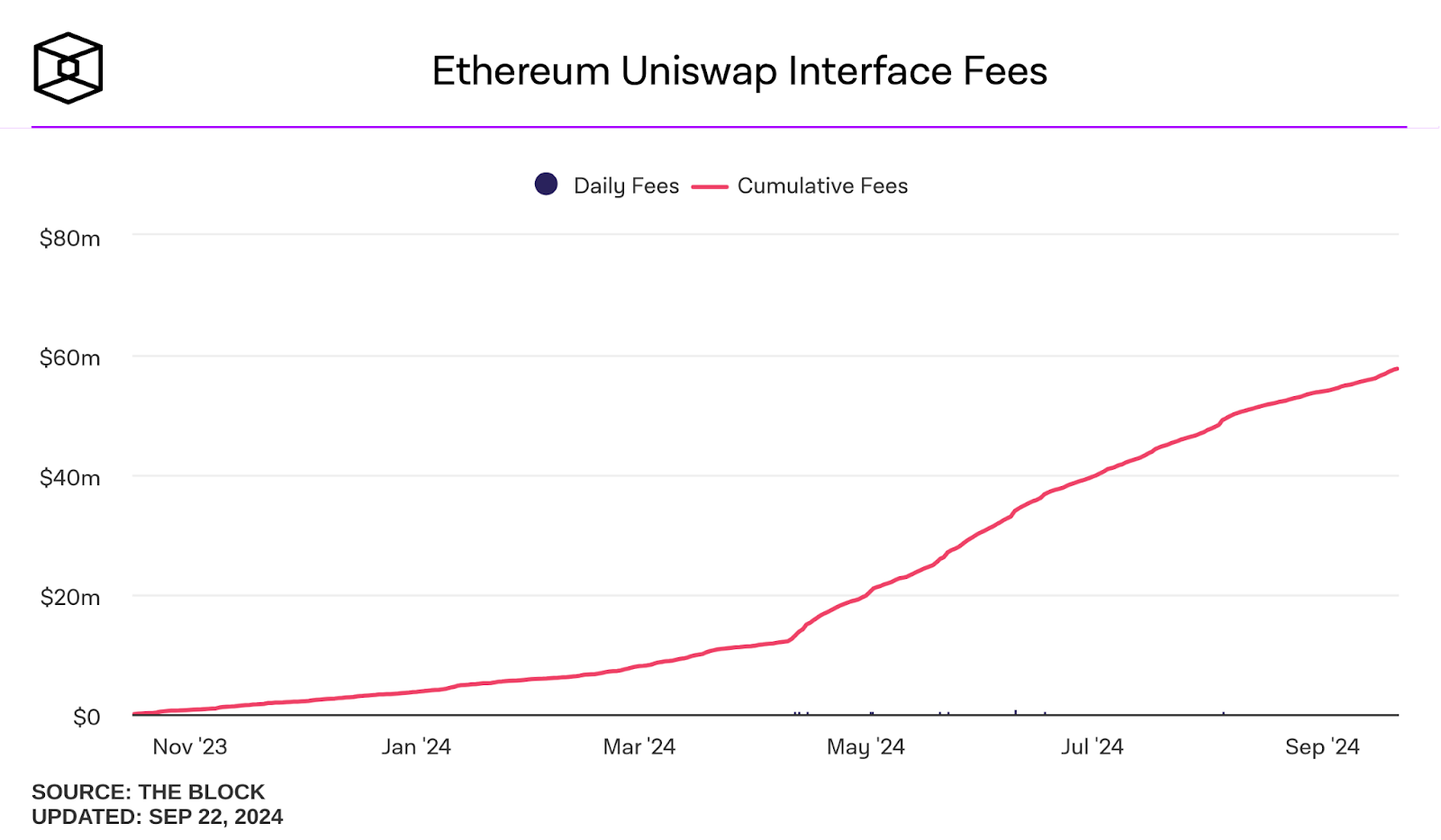
The daily amount of fees collected by Uniswap from traders using their web interface and wallet. Source: The Block Data
- Trading Fees: When using a DEX, you’ll need to pay a fee for each transaction, compensating liquidity providers for supplying the assets and facilitating trades. Unlike centralized exchanges, DEXs usually don’t differentiate between maker and taker fees, offering a more uniform structure. It’s crucial to compare fees among the leading DEX crypto exchanges to find one that offers competitive rates. Some platforms have lower trading fees but higher costs for withdrawals or deposits.
- Network Fees: You’ll also encounter network fees, which go to blockchain miners or validators to process your transactions. These fees vary based on the blockchain you’re using and current network congestion, so they can fluctuate.
- Withdrawal Considerations and Payment Methods: When considering a DEX, the ease of depositing and withdrawing funds is key—some platforms may integrate with third-party services to offer multiple payment methods, such as bank transfers, credit cards, or even PayPal. Having more payment options makes it more convenient to manage your funds and access liquidity when needed.
Why Choose Rubic for Decentralized Trading?

Rubic is a cross-chain DEX aggregator connected to over 200 decentralized exchanges and 15,500+ tokens. With a combined transaction volume of $887 million, Rubic simplifies the trading process by eliminating the need to manage multiple wallets or swap tokens on individual DEXs.
Key advantages include:
- Cross-Chain Swaps: Rubic enables seamless cross-chain swaps, allowing users to trade assets across different blockchain networks like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain (BSC), and Polygon, all from one platform. This simplifies portfolio diversification and eliminates the hassle of managing multiple wallets or exchanges.
- Best Rate Finder: As a DEX aggregator, Rubic searches for the best prices across 200+ decentralized exchanges in real time, ensuring users receive the most competitive rates, particularly in high-volume transactions. Rubic’s smart route optimization and liquidity aggregation are seamlessly integrated within MetaMask, making accessing the best crypto exchange rates and maximizing trading potential easier.
- Privacy-focused transactions: No registration is required, which protects user anonymity.
Rubic offers an efficient and user-friendly DEX platform, addressing many common challenges that users face. Learn more about how Rubic simplifies trading across multiple blockchains while ensuring the best rates and optimal liquidity.
Conclusion: The Future of DEXs
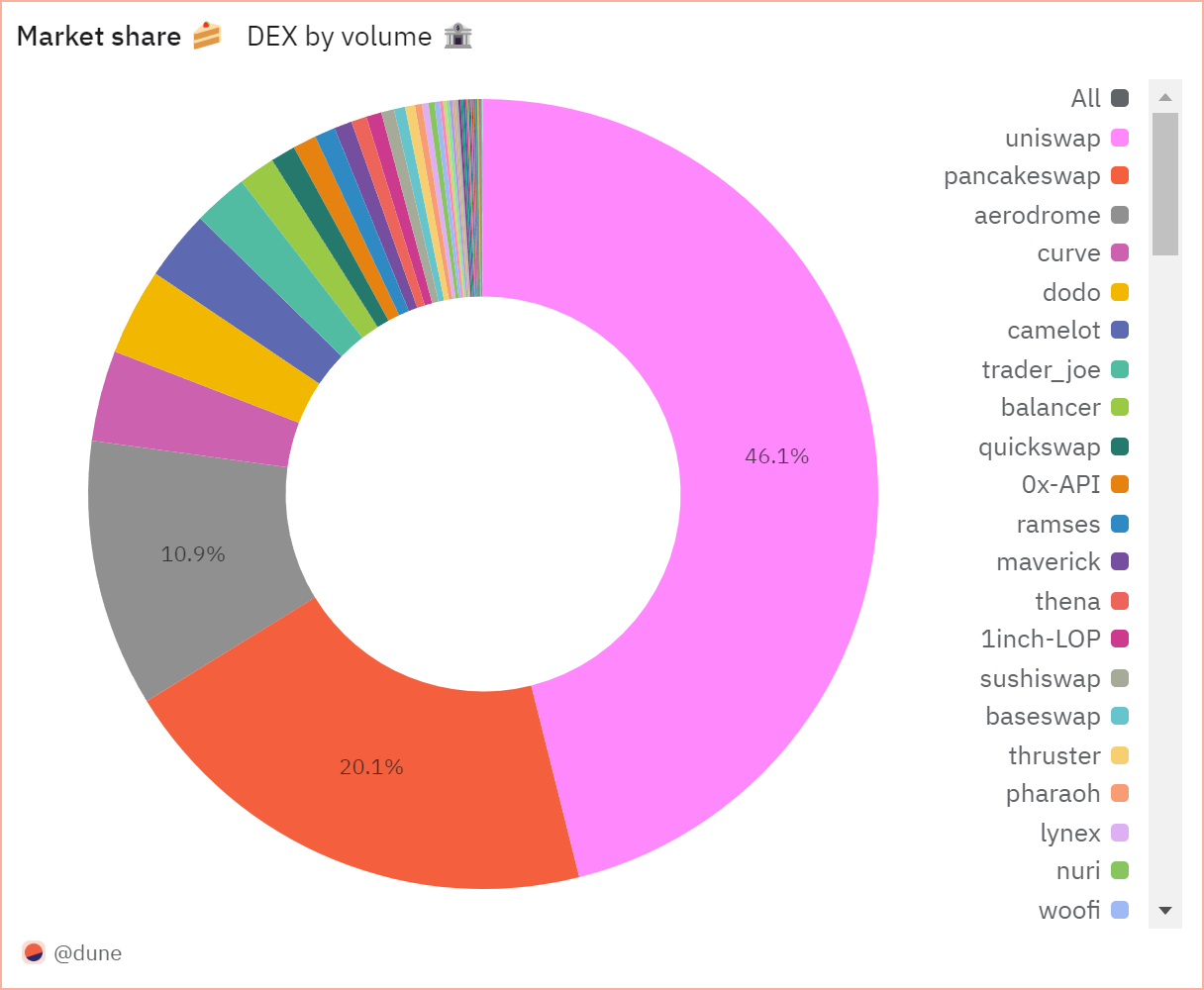
As platforms like Uniswap and PancakeSwap solidify their dominance, this trend underscores increasing user trust in decentralized exchanges. Here are a few critical trends shaping the space, particularly in terms of scaling, innovation, and aggregation:
- Layer 2 Solutions: Greater blockchain scalability is crucial for DEX growth, with Ethereum layer-2 solutions like Optimistic and ZK-Rollups paving the way for faster and cheaper transactions. This scalability is essential for handling higher volumes and reducing gas fees, which are key factors for DEX adoption and performance.
- DEX Aggregators and Liquidity Fragmentation: DEX aggregators are increasingly crucial in addressing fragmented liquidity across chains. By sourcing liquidity from multiple DEXs, they improve trading efficiency, reduce slippage, and optimize prices. For example, 1inch’s pathfinder algorithm pioneered this approach, making DEX aggregators vital in ensuring better trade execution.
- Market Makers and New Mechanisms: There is substantial innovation in market maker mechanisms, such as Concentrated Liquidity Automated Market Makers (CLAMMs) and Dynamic AMMs. These models are designed to boost capital efficiency and reduce impermanent loss, which are critical challenges for liquidity providers. Uniswap v3 and other DEXs incorporating these mechanisms have shown high turnover rates and trading volumes. DEX crypto has also introduced financial innovations like decentralized lending and borrowing, where users can lend their assets directly through smart contracts without a traditional bank. Another example is yield farming, which allows users to earn rewards by providing liquidity to specific token pairs.
- Bitcoin DeFi and Scaling Solutions: There is also a growing presence of DeFi on Bitcoin, with sidechains like Stacks and Rootstock (RSK) leading the way. Although still in its early stages, Bitcoin-based DEXs are gaining traction, with platforms like Sovryn achieving notable trading volumes.
The transparency, privacy, and direct control DEXs offer make a strong case for a decentralized future. Innovations in scaling, advanced market-making mechanisms, and liquidity aggregation steadily address current challenges and drive the ecosystem forward.
While issues like fragmented liquidity and high gas fees persist, these developments pave the way for greater efficiency, making DEXs a critical component of the cryptocurrency landscape.
As trust in centralized exchanges erodes, the demand for on-chain transparency and proof-of-reserves continues to grow. However, the shift to decentralized trading comes with its own responsibilities—managing your assets directly can be empowering, but it also means users must fully trust their ability to navigate the system. Ultimately, the future of decentralized trading will depend on how well we balance the desire for autonomy with the need for accountability.
FAQs About What Is a DEX
- What is the difference between a DEX and a CEX?
The key difference between a DEX and a CEX is user control and structure. In a DEX, users keep control of their funds, with trades executed via smart contracts, while CEXs require users to deposit funds into the exchange using a centralized order book. DEXs offer more privacy, often without KYC requirements, whereas CEXs usually require identity verification. CEXs typically provide faster trades and higher liquidity, while DEXs may have slower execution and lower liquidity for certain pairs. CEXs are also more regulated, while DEXs operate in a decentralized, less regulated environment.
- Are DEXs safe to use?
DEXs can be safe, but they come with certain risks. Smart contract vulnerabilities are a concern if the contracts aren’t properly audited. User responsibility is key, as individuals must secure their own wallets and private keys. Unlike CEXs, there’s no intermediary protection, so users have no recourse for mistakes or fraud.
- How do cross-chain swaps work on a DEX?
Cross-chain DEX swaps allow users to exchange tokens between different blockchain networks. This can be achieved through atomic swaps, wrapped tokens, liquidity pools, or bridge protocols that facilitate transfers across chains. The process typically involves smart contracts on both the source and target chains, but from the user’s perspective, it often appears as a single transaction.

