What Is Multi-Chain? Understanding the Blockchain Technology
Since the inception of Bitcoin and Blockchain technology, there have been multiple innovations to make it more economical and scalable. One such innovation that has gained significant traction in recent years is Multichain. But what exactly is Multichain, and how does it differ from traditional blockchain frameworks? Towards the end of this blog, you will have clarity about the intricacies of Multichain, exploring its history, functionality, importance, benefits, challenges, and its relationship with cross-chain technologies. We’ll also examine how platforms like Rubic are propelling the growth of the Multichain ecosystem and speculate on the future of this groundbreaking technology.
What Is Multi-Chain?
At its core, Multichain refers to a type of blockchain protocol or technology that enables the creation and operation of multiple interconnected blockchains within a single network. Unlike traditional blockchain frameworks that typically operate on a single chain, Multichain architectures offer enhanced scalability, interoperability, and customization capabilities. This flexibility allows developers and organizations to tailor blockchain solutions to meet specific use cases and business requirements more effectively.
Multi-chain technology enables different layers of different blockchain networks to communicate with each other seamlessly.
A Brief Look At the History of Multi-Chain
The concept of Multichain traces its roots back to the early days of blockchain development when pioneers like Satoshi Nakamoto introduced the world to Bitcoin, the first-ever cryptocurrency. While Bitcoin paved the way for decentralized finance, its limited scalability and functionality spurred the need for alternative solutions.
In response to these challenges, developers began experimenting with Multichain architectures, aiming to overcome the limitations of single-chain systems and unlock new possibilities for blockchain technology.
How Does Multi-Chain Work?
Multichain operates on a fundamentally different principle compared to traditional blockchain frameworks. Instead of relying on a single layer to record transactions and maintain consensus, Multichain networks consist of multiple interconnected chains, each serving a specific purpose or function.
There are basically two layers that operate in a Multi-chain blockchain technology. The consensus Layer verifies the transactions and ensures the security of the network and the Application Layer helps developers build Dapps (Decentralized Applications) that can communicate with different blockchain networks.
These chains can communicate and transact with one another seamlessly, enabling a higher degree of flexibility and scalability.
Why Is Multi-Chain Important?
The significance of Multichain lies in its ability to address some of the most pressing challenges facing blockchain technology today. By offering a more scalable and customizable infrastructure, Multichain networks empower developers to build robust decentralized applications (dApps) and enterprise-grade solutions that can scale to meet growing demand. Furthermore, Multichain architectures facilitate interoperability between different blockchain networks, fostering collaboration and innovation across the ecosystem.
Benefits of Multi-Chain
1. Scalability: Multichain networks can process a higher volume of transactions per second compared to traditional blockchain frameworks, thanks to their distributed architecture and parallel processing capabilities.
2. Interoperability: Multichain platforms enable seamless communication and data exchange between different blockchain networks, promoting synergy and collaboration within the ecosystem.
3. Customization: With Multichain, developers have the flexibility to tailor blockchain solutions to specific use cases and business requirements, allowing for greater innovation and experimentation.
4. Enhanced Security: By leveraging multiple chains for transaction validation and consensus, Multichain networks can mitigate the risk of network congestion, double spending, and other security vulnerabilities.
Challenges of Multi-Chain Technology
While Multichain offers numerous advantages over traditional blockchain frameworks, it also presents several challenges that must be addressed:
1. Complexity: Managing multiple interconnected chains can be complex and resource-intensive, requiring specialized expertise and infrastructure.
2. Security Risks: Interoperability between different blockchain networks can introduce security risks such as cross-chain attacks and data breaches if not implemented correctly.
3. Governance: Determining governance models and consensus mechanisms across multiple chains can be challenging, leading to potential conflicts and coordination issues.
4. Adoption Barriers: Despite its potential, Multichain adoption still faces barriers such as regulatory uncertainty, interoperability standards, and scalability limitations.
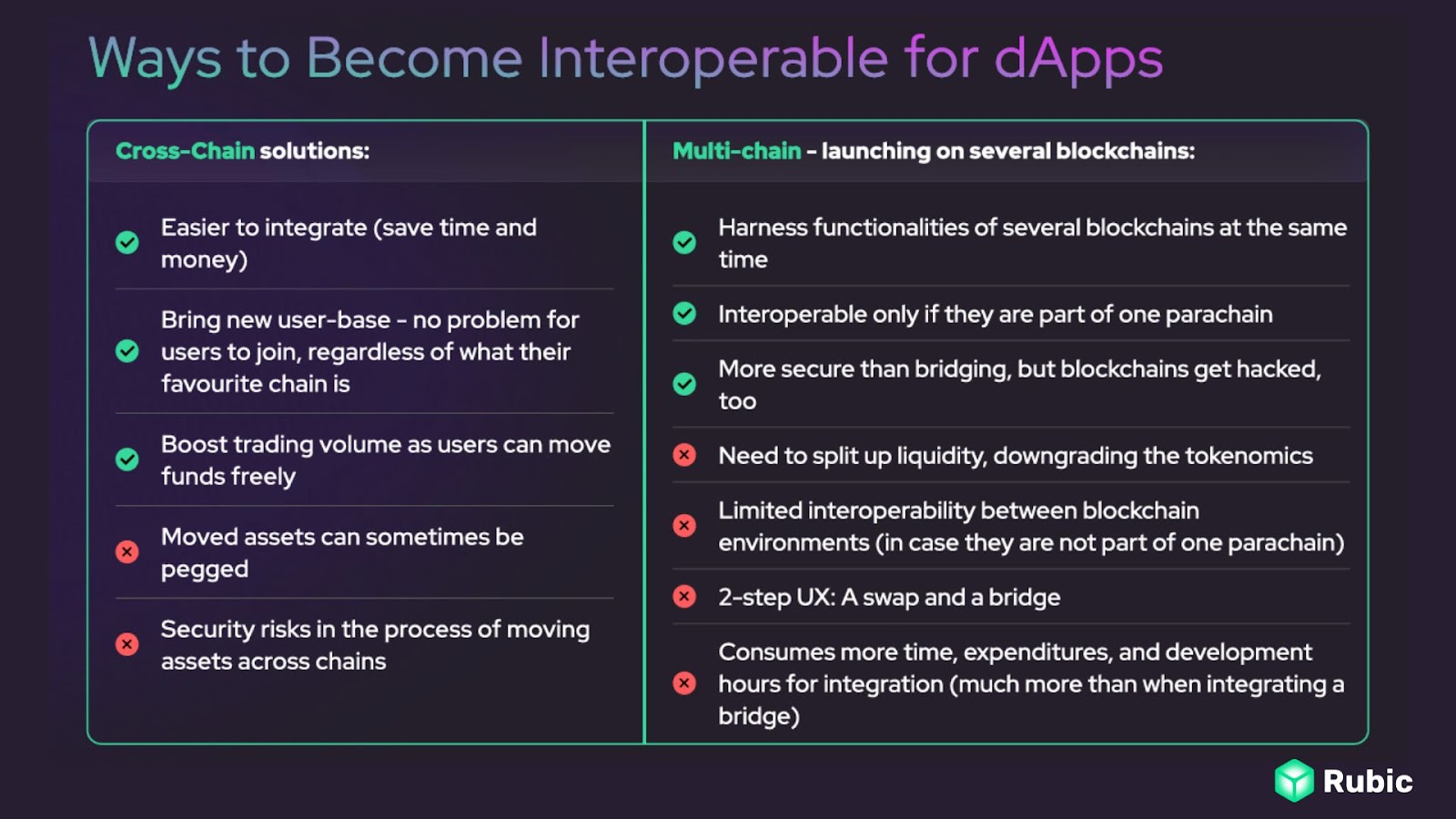
Multi-Chain vs Cross-Chain
It’s essential to distinguish between Multi-chain and Cross-chain technologies, as they serve distinct purposes within the blockchain ecosystem. While Multichain refers to the creation and operation of multiple interconnected chains within a single network, cross-chain technologies focus on facilitating communication and asset transfer between different blockchain networks.
To explain it better, Cross-chain allows assets to flow between unrelated blockchains with the help of smart contracts and Multichain refers to projects based on several blockchains (either with a single consensus layer or completely separated). In other words, Multichain is about building a cohesive ecosystem of interconnected chains, whereas cross-chain technologies enable interoperability between independent blockchains.
How Rubic Supports a Multi-Chain Ecosystem
Rubic is a prime example of a platform that supports and accelerates the growth of the Multichain ecosystem. By providing tools and infrastructure for developers to build, deploy, and manage Multichain applications, Rubic empowers innovation and collaboration within the blockchain community. Through its intuitive interface and robust feature set, Rubic simplifies the development process and facilitates seamless integration with existing blockchain networks. Whether it’s launching a new token, creating a decentralized exchange, or implementing cross-chain interoperability, Rubic offers a comprehensive suite of solutions to meet the diverse needs of Multichain developers and users alike.
Final Thoughts: The Future of Multi-Chain
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, Multichain is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of decentralized finance, digital assets, and beyond. With its ability to enhance scalability, interoperability, and customization, Multichain holds the potential to unlock new opportunities for innovation and adoption across various industries. However, realizing this potential will require collaboration, experimentation, and ongoing development to address the challenges and barriers hindering Multichain adoption. Nevertheless, the future looks bright for Multichain, and its transformative impact on the blockchain ecosystem is only just beginning.
Explore the potential of multi-chain technology on Rubic cross-chain swap today!
FAQs About Multi-Chain
What is a multi-chain used for?
Multichain is used to create and operate multiple interconnected blockchains within a single network, enabling enhanced scalability, interoperability, and customization for decentralized applications and enterprise solutions.
What is the difference between blockchain and multi-chain?
While blockchain refers to a single chain of blocks containing transactional data, Multichain involves the creation and operation of multiple interconnected chains within a single network, offering greater flexibility, scalability, and interoperability.
What is an example of a multi-chain?
Ethereum is a prominent example of a Multichain platform that supports the creation and deployment of multiple interconnected chains, known as sidechains or layer 2 solutions, to enhance scalability and functionality. Additionally, projects like Polkadot and Cosmos are dedicated to building interoperable Multichain ecosystems that facilitate communication between different blockchain networks.

