Bitcoin Layer 2: What Is It & Must-Know Projects in 2024

TL;DR
- Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions enable fast, low-cost micropayments by using off-chain channels.
- Transactions on L2s can be settled within seconds, compared to the main blockchain’s longer processing times.
- By enabling asset swaps between Bitcoin and other chains, L2 solutions enhance interoperability, allowing users to interact with multiple decentralized apps and protocols in a seamless, efficient manner.
- Offloading transactions to sidechains and rollups helps reduce congestion on Bitcoin’s main blockchain, which also lowers fees for users and improves overall scalability.
- The long-term success of Layer 2s will depend on their ability to adapt to market shifts and maintain user engagement, with only a few likely to thrive.
What Is Bitcoin Layer 2?
Bitcoin Layer 2 (L2) refers to a secondary protocol built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain, designed to enhance scalability and improve transaction speed. It facilitates off-chain transactions, meaning the exchange happens outside of the main blockchain. This relieves congestion on the Layer 1 network and significantly reduces transaction fees.
It takes on the bulk of the work—processing transactions off-chain—before handing it back to the Layer 1 blockchain for the official record. This makes everything run faster and smoother, all while ensuring the integrity of the main network. Think of Layer 2s as extra lanes added to a busy highway—they run on top of the main blockchain, designed to ease the traffic and speed things up. By bypassing the technical limits of Bitcoin’s core network, these secondary layers can handle more transactions without losing any of the strengths that make Bitcoin so secure.
Why Does Bitcoin Need Layer 2s?
Bitcoin is often called “digital gold” for a reason—it’s one of the most trusted ways to store value. But here’s the thing: even though Bitcoin was initially designed to be a secure, decentralized payment system, it hasn’t exactly taken off as a daily payment method. Why? Well, that’s where its limitations come in.
Bitcoin itself works well for what it was designed to do—solving the double-spend problem and securing the network. It doesn’t need to change much in that regard. However, the base layer can only handle so many transactions at a time, and that makes using Bitcoin for everyday purchases slow and expensive. In short, Bitcoin itself doesn’t need to change much—but the infrastructure around it does, and that’s where Layer 2 solutions can make a huge difference.
Let’s Talk Scalability
Ever tried to send a Bitcoin transaction and wondered why it takes so long? You’re not alone. Bitcoin faces fundamental scalability challenges. Its original network design processes only around seven transactions per second (TPS), which, compared to blockchains like Solana that can handle thousands of TPS, feels like a snail’s pace. As a result, the network often becomes congested, leading to slower transaction speeds and higher fees. To put it in perspective, creating a block takes about 10 minutes, meaning a small transaction, like buying a cup of coffee, can take longer to finalize than it would to just pay with a card.
Now, if you’re moving a large sum of money, that delay may not bother you. Still, it’s not ideal for smaller, everyday purchases, such as purchasing an Ordinal NFT or sending a few satoshis to access premium content.
To provide some context:
- In 2016, the average Bitcoin transaction fee was around $0.07. Fast forward to 2024, the typical transaction fee on Bitcoin’s Layer 1 can be approximately $20 per transaction. And it gets worse during periods of congestion on the network, such as in April 2024 when trading volume grew right before the Bitcoin halving event.
- The typical transaction fee on Bitcoin Layer 2 can be much smaller, averaging around $0.00003 per transaction.
- Although Bitcoin’s Layer 1 can manage approximately seven transactions per second, Layer 2 protocols can process over 5,000 transactions per second.
- While a typical Bitcoin Layer 1 transaction takes approximately 10 minutes for confirmation, transactions on Layer 2s are usually confirmed in a few seconds.
(For a deeper dive into these fee hikes, check out the data from YCharts)
Why Can’t Bitcoin Scale?
It all boils down to what’s known as the Blockchain Trilemma—the idea that you can’t have decentralization, security, and scalability all at once. Bitcoin chose to prioritize decentralization and security, which is why it’s such a strong and tamper-resistant network. But the trade-off is that it can’t scale easily. Trying to expand its capacity would likely mean compromising the very features that make Bitcoin so secure and decentralized in the first place. It’s a tough balance to strike.
Then there’s the issue with smart contracts.
Unlike Ethereum, Bitcoin wasn’t designed with smart contracts in mind. It’s great at what it does—enabling peer-to-peer transactions and acting as a deflationary store of value. But it’s not built for complex applications like decentralized finance (DeFi) or NFTs. While Ethereum powers an entire ecosystem of decentralized applications (dApps), Bitcoin’s base layer is much more limited by design—a feature that makes Bitcoin stable and secure.
However, it also means that Bitcoin has yet to venture into the world of smart contracts or dApps. This raises the question: how can Bitcoin become a practical option for everyday transactions, especially in a world moving towards DeFi?
Here is where Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions (BTC L2s) come into play to tackle these challenges.
How Do Bitcoin Layer 2s Work?
Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions are built to supercharge the network’s scalability and efficiency by moving transactions off the main blockchain. This not only lightens the load on the primary network but also speeds up transactions and makes them cheaper. Layer 2s rely on mechanisms like state channels, rollup chains, and sidechains, each bringing unique advantages and functionalities to the table.
State Channels
State channels are private channels that allow multiple parties to transact off-chain. Participants open a channel by locking a certain amount of Bitcoin in a multi-signature wallet. They can then transact freely within this channel without broadcasting each transaction to the Bitcoin blockchain. Only the opening and closing balances are recorded on-chain, which significantly reduces the number of transactions that need to be processed by the main network.
However, state channels are limited in not supporting complex smart contracts, which can restrict their use cases.
Sidechains
Sidechains are independent blockchains that run parallel to the Bitcoin main chain. Assets can be transferred between the main chain and the sidechain through a two-way peg. This means that Bitcoin can be locked on the main chain, and an equivalent amount of a synthetic asset can be issued on the sidechain.
Sidechains operate under their own rules and consensus mechanisms, allowing for features like smart contracts and different transaction types without affecting the main Bitcoin network. They enable developers to test new protocols and functionalities, encouraging innovation.
Rollup Chains
Rollups are a Layer 2 solution that allows multiple transactions to be bundled and processed off-chain, reducing the load on the Bitcoin main chain.
There are two main types of rollups: Optimistic Rollups and Zero-Knowledge (ZK) Rollups. Optimistic Rollups assume transactions are valid and only check them if a dispute arises, while ZK-Rollups use cryptographic proofs to verify transactions without revealing their details. Both methods significantly reduce the amount of data that needs to be stored on the main chain.
BitVM, introduced in 2022 by Robin Linus, is a trust-minimized approach to ZK-Rollups, which allows for secure interactions with the Bitcoin blockchain. Rather than making Bitcoin a DeFi platform similar to Ethereum, it focuses on running smart contracts off-chain to reduce the pressure on the blockchain while preserving Bitcoin’s core principles of decentralization and security.

Image source: https://www.blog.citrea.xyz/introducing-citrea/
Launched in February 2024, Citrea, incubated by Chainway Labs, is the first implementation of ZK-Rollup technology specifically for Bitcoin, making it a big leap in Bitcoin’s scalability. It operates as an execution layer on Bitcoin, using ZK proofs and BitVM to maintain data availability and settlement on the main chain. Acting as an execution layer, Citrea uses ZK proofs and BitVM to ensure data availability and settle transactions directly on Bitcoin’s main chain—allowing Bitcoin to scale while maintaining its core values of security and decentralization. Chainway has also open-sourced its data availability (DA) adapter, giving developers the tools to build rollups on Bitcoin’s secure foundation using the Sovereign Software Development Kit (SDK).
Other projects are exploring similar paths. Brollups, is another layer-2 solution that’s still in the works, with its own approach to scaling Bitcoin. Sovryn’s Bitcoin OS is taking things further by building a superchain of Bitcoin rollups, enabling different rollups to interact and share resources—expanding Bitcoin’s capabilities for dApps.
What Is the Difference Between Bitcoin and Ethereum Layer 2s?
The main difference between Bitcoin and Ethereum Layer 2 solutions lies in what they’re built to handle. Bitcoin Layer 2s, like the Lightning Network, are about scaling payments and making transactions faster and cheaper. On the other hand, Ethereum’s Layer 2s—like Polygon, Optimism, and Arbitrum—focus on supporting smart contracts and dApps, offering much more versatility.
Additionally, Bitcoin Layer 2 protocols must create their own environments since they don’t have the same level of smart contract support as Ethereum, which uses its Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) for compatibility across its ecosystem. Bitcoin’s scripting is also more limited, which restricts the complexity of its Layer 2 solutions, whereas Ethereum Layer 2s thrive in building out complex applications like DeFi and NFTs.
So, while both aim to improve scalability, they serve very different purposes.
| Key Differences | BTC L2s | ETH L2s |
| Settlement Layer | Built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain | Based on the Ethereum blockchain |
| Objectives | Increase speed, lower fees, add limited programmability | Scalability, lower costs, and support for smart contracts and dApps |
| Technologies | State channels and sidechains | Sidechains and rollups |
5 Key Bitcoin Layer 2 Projects to Watch in 2024
In 2024, Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions are gaining significant traction in the market, driven by the demand for faster, more scalable, and secure networks. This section will highlight the top five BTC L2 projects to follow, evaluated through a mix of methodologies, including Total Value Locked (TVL), which indicates the capital locked within these networks, and user adoption, reflecting the number of active participants.
We also consider each project’s utility—how well they enhance Bitcoin’s core functionality, such as enabling smart contracts or improving transaction speeds. Technological advancements, like the integration of ZK-Rollups or EVM compatibility, and their impact on Bitcoin’s scalability are equally important. Security measures are also crucial, as these projects leverage Bitcoin’s proof-of-work security or introduce new mechanisms to ensure decentralized, trustless environments.
1. The Lighting Network (LN)
The Lightning Network is the largest Bitcoin Layer 2 solution, with over $322 million in TVL (at the time of writing), and can theoretically handle up to 1 million transactions per second, compared to the main chain, which handles about seven transactions per second. Launched in 2018, it has become a cornerstone of Bitcoin’s scalability efforts.
Lightning is designed to facilitate fast and low-cost transactions by creating payment channels between users. This capability has made it a preferred choice for micropayments and everyday transactions.
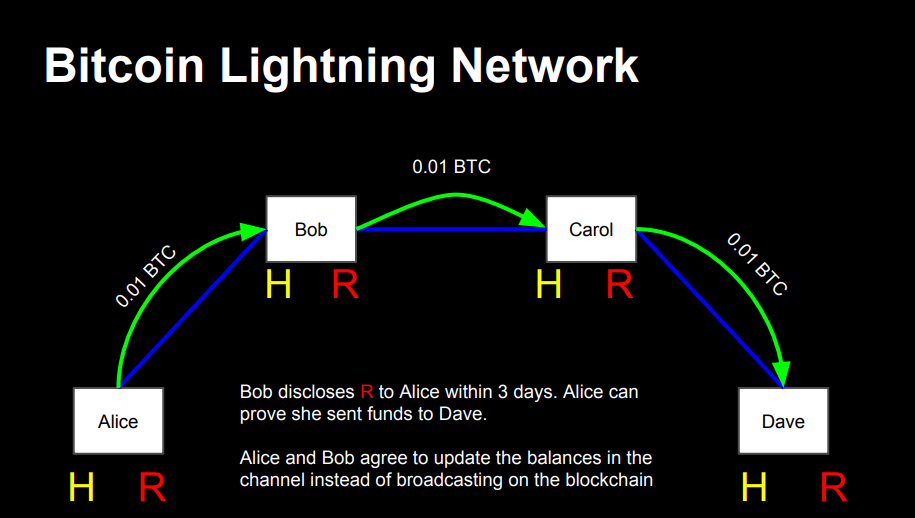
Image source: https://lightning.network/lightning-network-presentation-time-2015-07-06.pdf
Additionally, integrating Lightning in platforms like X for Bitcoin tips showcased its practical application in real-world scenarios, demonstrating its efficiency and speed. At the 2024 Bitcoin Conference in Nashville, key advancements in the Lightning Network took center stage, underscoring the rapid maturation of this technology as it gears up for broader adoption and strengthens bullish momentum.
Key Features:
- Instant Transactions: Enables near-instant Bitcoin payments by processing transactions off-chain.
- Low Fees: Reduces transaction costs significantly, making it ideal for micropayments.
- Scalability: Can handle millions of transactions per second, far beyond Bitcoin’s base layer.
- Payment Channels: Allows users to open private channels for multiple transactions without settling each on the blockchain.
Recent Advancements:
- With Taproot Assets now live on the mainnet, users can make instant, low-fee asset transfers, bringing trillions of stablecoin volume to Bitcoin. This advancement opens access to global currencies on an open, interoperable payments network, all routed through Bitcoin liquidity.
- The network allows for the opening of larger “Wumbo” channels. Initially, Lightning channels were capped at 0.1677 BTC, but that restriction has been lifted, and users can now transact larger amounts.
- Integration with major crypto exchanges like Kraken and Coinbase.
- The introduction of “watchtowers” (third-party nodes) to prevent fraud and ensure secure transactions.
Critical Challenges:
- Merchant adoption and user understanding remain limited due to its complexity and the technical expertise required to manage liquidity and payment channels effectively.
- Nodes must remain online at all times, exposing them to security vulnerabilities.
- Potential security issues, including double-spending and offline nodes disrupting payments.
- Concerns about centralization as the network grows and routing becomes more dominant.
2. The Liquid Network (LQ)
The Liquid Network is a sidechain that operates on the open-source Elements blockchain platform, designed for faster transactions between exchanges and institutions. It is governed by a distributed federation of Bitcoin companies, exchanges, and other stakeholders. It uses a two-way peg to convert BTC to L-BTC and vice versa.
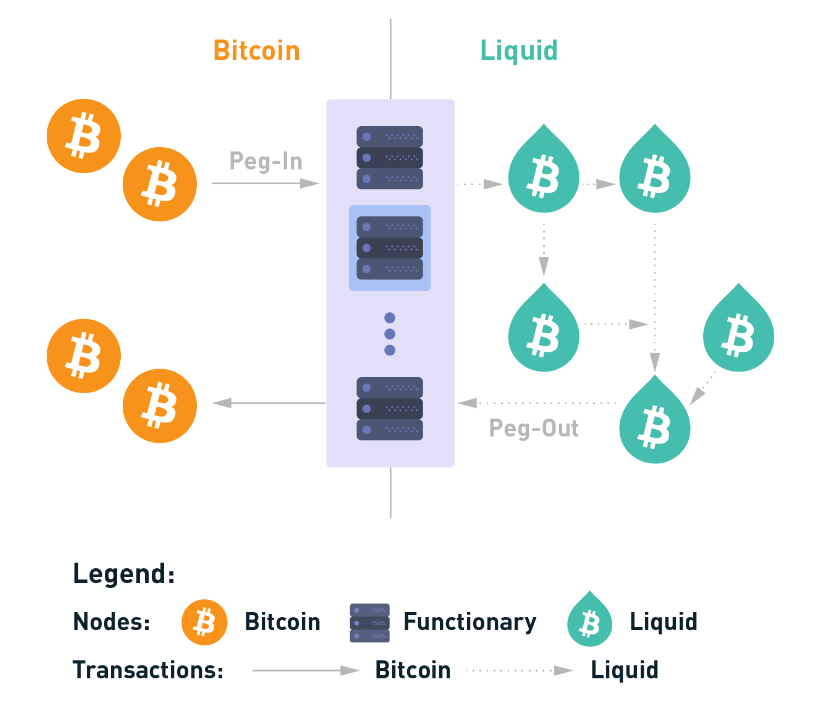
Image source: https://docs.liquid.net/docs/technical-overview
Liquid allows for confidential transactions and supports tokenization, making it suitable for enterprise applications. Suppose Bitcoin is the value layer of the internet and Lightning is the peer-to-peer payments network of a Bitcoin-powered financial system. In that case, Liquid is the financial layer, adding multi-asset support and financial instruments, like securities and commodities, into the mix.
Compared to Lightning, Liquid is a Bitcoin layer 2 solution focused on facilitating larger, more complex transactions such as issuing and trading assets like securities and stablecoins. Liquid has built-in confidential transactions, hiding the amount and type of assets, whereas Lightning offers privacy primarily through its off-chain transactions. While Lightning excels in microtransactions and everyday payments, Liquid is better suited for institutional finance, asset issuance, and cross-border trading.
With over 50 exchanges adopting the Liquid Network, it has facilitated billions of dollars in transactions, proving its effectiveness in enhancing Bitcoin’s utility for institutional trading. The Liquid Network’s ability to provide faster settlement times for exchanges has improved liquidity in the Bitcoin market, allowing institutions to operate more efficiently and securely.
Key Features:
- Fast Settlements: Its native asset, L-BTC, settles in under two minutes, far quicker than Bitcoin’s base layer.
- Confidential Transactions: Liquid hides transaction amounts and asset types by default, ensuring privacy and protecting sensitive financial information from public exposure.
- Secure Tokenization: The Liquid Network allows for the secure issuance of tokens representing fiat currencies, securities, or digital assets directly on its sidechain. This capability facilitates a wide range of financial applications and enhances the flexibility of asset management.
- Interoperability: Liquid supports seamless interoperability through a single integration that accommodates both L-BTC and issued assets. This functionality enables atomic swaps and multi-signature transactions, enhancing the overall user experience and facilitating cross-asset transactions.
Recent Advancements:
- The launch of the new Liquid Wallet Kit, with its modular design and support for advanced features, such as confidential transactions, atomic swaps, and cross-chain swaps, represents a significant advancement in the growth of DeFi applications on the Liquid network.
- Daedalus Labs is developing RESIN, a platform that uses Liquid to enable real estate investments through a rent-to-own model, bridging Bitcoin with tangible assets.
- DitoBanx, a Bitcoin fintech company in El Salvador, plans to issue several financial assets on the Liquid Network, aiming to create a circular Bitcoin economy in Latin America.
- eNor Securities, a regulated exchange for tokenized assets, has integrated with Liquid to provide a compliant environment for digital asset trading, leveraging Liquid’s multi-signature wallet capabilities.
Critical Challenges:
- The current liquidity may not be enough to attract traders and users, which can limit its effectiveness as a trading platform.
- The Liquid Network operates on a federated model, which differs from Bitcoin’s decentralized nature. Exchanges must trust the functionaries that validate transactions, raising concerns about security and reliability.
- Many smaller exchanges lack the necessary resources or technical expertise to integrate the Liquid Network effectively into their operations, which can be complex and resource-intensive.
- The network’s reliance on a federated model could lead to centralization, which may undermine the core principles of Bitcoin.
3. Rootstock Infrastructure Framework (RBTC)
Rootstock is the longest-running Bitcoin sidechain since its birth in 2015 and the launch of its mainnet in 2018. It’s unique because it combines Bitcoin’s proof-of-work (PoW) security with Ethereum’s smart contracts. As an open-source, EVM-compatible Bitcoin Layer 2 solution, Rootstock serves as a gateway to a growing dApp ecosystem, striving to become fully trustless.
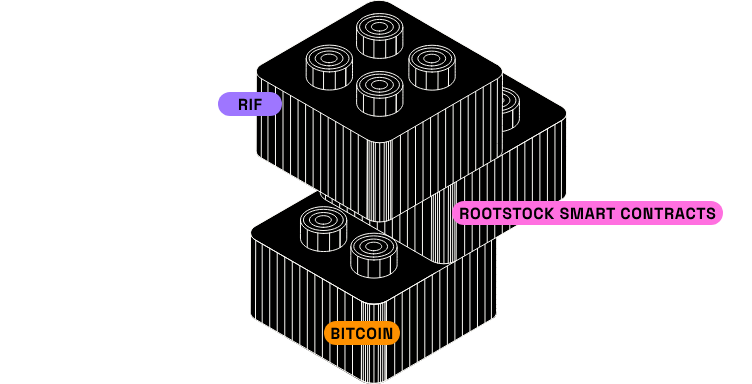
Image source: https://dev.rootstock.io/concepts/fundamentals/stack/
Like Liquid, Rootstock uses a two-way peg, so you can easily swap between BTC and RBTC, the native currency used on the RSK blockchain to pay miners for transaction and contract processing. While Liquid is more about fast, private transactions and asset issuance, Rootstock is about expanding Bitcoin’s DeFi and dApp ecosystem through smart contracts.
At the time of writing, Rootstock currently has over $170 million in TVL with a market cap of $380 million.
Key Features:
- BTC as Native Token: RBTC allows users to interact with DeFi protocols and dApps on the Rootstock network. Pegged 1:1 to Bitcoin, users can lock BTC on Bitcoin, mint an equal amount of RBTC on Rootstock, and it’s a 1:1 swap.
- Secured by Bitcoin Proof of Work: Rootstock is secured by over 50% of Bitcoin’s hashing power through merged mining, which allows Bitcoin miners to mine both Bitcoin and RBTC simultaneously without additional resources.
- Uncensorable Bitcoin Peg: Rootstock runs on the same PoW system as Bitcoin using the PoWPeg protocol, a two-way peg that lets users easily swap BTC and RBTC. It uses Bitcoin’s consensus rules and specialized hardware (PowHSMs) to keep the process secure, decentralized, and censorship-resistant.
- Interoperable with Ethereum: The Rootstock blockchain is fully EVM compatible at multiple layers, including smart contract programming in Solidity and the web3.js JavaScript interface. This allows developers to deploy Ethereum contracts directly on Rootstock with minimal changes.
| Bitcoin BTC | Liquid LBTC | RSK RBTC | |
| Average confirmation time | 10 min | 60 sec | 15 sec to 30 sec |
| Security threshold (due to selfish mining or collusion) | ~30% | 50% | 50% |
| Turing complete smart-contracts | No | No | Yes |
| Add value to Bitcoin | – | Yes | Yes (merge-minded) |
| Integration with Bitcoin | – | Sidechain | Sidechain |
| Hardware wallet integration | Yes | No | Yes |
| Scalability (tps) | 3 (6 with sedwit) | 3 (6 with sedwit) | Unbounded currently 10 |
| Confidential transactions | No | Yes | Via contract. Native support planned |
| Blockchain size | 200GB | ~300 MB | ~2 GB |
| Token peg security | – | Federation | Federation |
Recent Advancements:
- Rootstock has seen multiple integrations with DeFi platforms, including Balmy, Gelato, and CoNFT. These integrations aim to enhance user experiences by providing decentralized banking solutions, automated workflows, and user-friendly platforms for minting NFTs.
- The launch of OpenOcean’s DEX aggregator on Rootstock offers traders new opportunities to leverage the strengths of both Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Rootstock continues to bolster its security through merged mining, which enables it to tap into Bitcoin’s massive hashing power. According to a Q1 2024 report, there has been a notable increase in participation from Bitcoin mining pools, further securing the network.
- Rootstock World Tour is a series of events hosted on the Galxe Quests platform to promote user adoption and development of dApps featuring interactions with 10 dApps in the Rootstock ecosystem: Oku, Symbiosis, Sushi, Woodswap, CoNFT, Money On Chain, Rubic Exchange, Tropykus and Sovryn.
Critical Challenges:
- As Rootstock grows, the potential for a few mining pools to dominate could threaten the decentralized nature of the network.
- Implementing smart contracts on Rootstock presents technical hurdles as developers transitioning from Ethereum face difficulties adapting to the new environment.
- Rootstock operates in a highly competitive landscape with other BTC L2s. To remain relevant, Rootstock must differentiate itself by focusing on niche applications and enhancing user engagement.
- If RBTC does not maintain sufficient liquidity, it may struggle to achieve a stable market price, making it a riskier investment option and deterring users.
4. Merlin Chain (MERL)
Merlin, launched in January 2024, is a Bitcoin-native, EVM-compatible Layer 2 rollup network that integrates several advanced technologies like ZK-Rollups, a decentralized oracle network, Data Availability, and on-chain BTC fraud-proof modules. The network supports both Bitcoin and Ethereum protocols, along with token standards like BRC-420 and ERC.
Unlike other EVM Bitcoin L2s, users can access Merlin directly through their Bitcoin wallets, thanks to BTC Connect, a protocol developed by Particle Network. It also supports EVM wallets like MetaMask.
With a goal to “Make Bitcoin Fun Again,” there are currently over a hundred dApps live in its ecosystem, from DeFi and gaming to infrastructure and NFTs. According to DefiLlama, Merlin has over $137 million in TVL, while Merlin’s Seal—a campaign where 20% of the total supply of $MERL tokens will be airdropped to participants—currently has a TVL of $947 million.
Image source: https://merlinchain.io/
By leveraging ZK-Rollups, Merlin batches thousands of transactions on its execution layer for final settlement on the Bitcoin blockchain, achieving both speed and cost-efficiency without sacrificing Bitcoin’s security. Thanks to its EVM compatibility, developers can deploy Ethereum and EVM-based apps on Merlin without major code changes.
The team behind Merlin, Bitmap Tech (formerly Recursiverse), is a top-tier OG team with a market cap surpassing $500 million, backed by investors like OKX Ventures. The BRC-420 “Blue Box” collection under Bitmap Tech is currently valued at a floor price of $1.4k after peaking at $40,000 in February 2024. Minted for just $1 in September 2023, it’s the third largest 10k NFT series, trailing only BAYC and Punks.
Although Merlin offers a great BTC L2 solution, the project is relatively new and highly speculative. Most of the technologies and features still need to be fully implemented.
Key Features:
- Low Fees, High Scalability: Merlin Chain delivers low fees and high scalability as an EVM-compatible chain, ensuring fast transaction processing and improved liquidity.
- Support for Bitcoin Protocols: Merlin Chain supports key Bitcoin protocols like BRC20, BRC420, Bitmap, Atomicals, Pipe, and Stamp, allowing a wider range of users to engage with Bitcoin Layer 2.
- ZK-Rollup on Bitcoin: Merlin Chain boosts scalability and efficiency by implementing ZK-Rollup. Sequencer nodes manage data transmission through decentralized oracles, ensuring both transparency and security.
- On-Chain BTC Fraud Proofs for Enhanced Security: By leveraging Bitcoin’s consensus mechanism, Merlin’s fraud-proof modules allow users to challenge and resolve disputes directly on the Bitcoin blockchain, reinforcing the network’s security and trust.
Recent Advancements:
- Listings of its native token, $MERL, on multiple crypto exchanges. As a BRC-20 token, $MERL is the third of its kind to be featured on OKX.
- Other noteworthy listings include Bitget, Gate.io, Kucoin, WOO X, ByBit, BingX, and MEXC. This expansion highlights Merlin Chain’s robust growth and the community’s strong support, which has been instrumental in its development.
- Rubic Exchange integrated with Merlin Chain to enhance user engagement via participation in a 3,000,000 $MERL prize pool for cross-chain and on-chain swaps with zero protocol fees.
- Merlin Chain partners with Ordinal Hive to create the first Ordinal trading protocol to address a significant gap in the current market landscape for Bitcoin-based asset trading, which primarily caters to retail investors. The partnership aims to fill that void by creating a dedicated trading platform tailored to the needs of high-frequency and high-volume traders.
Critical Challenges:
- While Merlin uses ZK-Rollups to scale, Bitcoin’s Turing incompleteness complicates complex computations, requiring more innovative solutions to maintain performance and security.
- Merlin’s decentralized oracle network (where ensuring the trustworthiness of oracle nodes is usually up to the community) and on-chain BTC fraud-proof mechanisms add complexity to security, requiring careful oversight.
- As of the latest data, Merlin Chain has shown limited growth in active addresses since its inception, lagging behind both Ethereum layer-2 solutions and the Bitcoin network. This limited growth suggests that it may not be attracting new users or retaining existing ones effectively.
- Currently, 74.9% of MERL tokens are locked, limiting market liquidity and reducing user incentives to engage with the network. As tokens gradually unlock through 2025, there’s potential for increased trading and user engagement.
5. Stacks Protocol (STX)
Stacks has emerged as a leading Bitcoin Layer 2 solution since its launch on the mainnet in 2018 as Blockstack.

Image source: https://docs.stacks.co/stacks-101/proof-of-transfer
Stacks connect directly to Bitcoin and enable smart contracts, dApps, and NFTs to be built on Bitcoin, significantly expanding Bitcoin’s functionality beyond just a store of value. It uses a unique Proof of Transfer (PoX) consensus mechanism that ties its security directly to Bitcoin without modifying Bitcoin itself.
With over $99 million in TVL, Stacks’ established infrastructure and growing developer community make it a must-watch in the space.
Key Features:
- Layered Architecture: This design allows Stacks to add smart contracts and programmability on top of Bitcoin’s foundational layer, enhancing its capabilities without complicating Bitcoin itself. In contrast, the Lightning Network primarily focuses on scaling existing Bitcoin transactions without introducing new functionalities, while Liquid operates as a federated sidechain with its own governance structure.
- Proof of Transfer (PoX): Stacks employs a mechanism called Proof of Transfer (PoX), which links its operations directly to Bitcoin. This process allows Stacks to leverage Bitcoin’s security and immutability by recording its entire transaction history on the Bitcoin blockchain.
- Unique Token Model: Stacks has its native token, STX, which does not represent pegged Bitcoin.
- Decentralization and Censorship Resistance: Stacks’ design decisions operate under the idea that decentralization is more important than rejecting altcoins.
Recent Advancements:
- The Nakamoto upgrade is underway and promises fundamental changes in how Stacks works for increased transaction throughput and 100% Bitcoin finality.
- Stacks emerged as a leader among other Bitcoin L2s, experiencing a surge of nearly 20% post-halving, reaching approximately $2.87 and outperforming BTC (which only increased by approximately 4.7% during the same period).
- Stacks has seen a steady rise in TVL, indicating increased adoption of its platform. Stacks has established bridges to Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain (BSC), expanding its reach and opportunities for developers.
- The integration of sBTC, a pegged Bitcoin token, enhances the functionality of Stacks by allowing users to interact with Bitcoin directly within the Stacks ecosystem.
Critical Challenges:
- Stacks transaction confirmations are tied to slower Bitcoin block times, leading to high latency. Stacks must wait for Bitcoin’s sortition process to elect a miner before producing a new block.
- Microblocks were meant to improve transaction inclusion times but have proven ineffective. The protocol does not guarantee that microblocks will be confirmed before the next sortition, leading to orphaned transactions.
- Stacks forks are not inherently tied to Bitcoin forks, making it easy to reorganize the Stacks chain. This allows miners to manipulate the chain, posing security risks.
- Poor connectivity among miners can cause orphaned blocks when some miners don’t receive the canonical chain tip in time. Bitcoin miners may also deliberately exclude Stacks miners’ block-commits.
Addressing the Risks of Using Bitcoin Layer 2s
While BTC L2s offer benefits such as faster transactions and lower fees, they also introduce new potential points of failure, security vulnerabilities, and other risks, including fragmented liquidity, dependence on off-chain mechanisms, and potential centralization. Below are some important steps that you can take to keep things safer when using Layer 2 networks, whether as a user or developer:
Conducting Thorough Research
Before engaging with any Layer 2 solution, take the time to understand the tech behind it. Dig into the protocols, check out the development team, and familiarize yourself with the system. Knowing the architecture and security measures will help you spot any red flags.
Use Reputable Wallets and Services
Always go with well-established wallets and services with a solid track record of supporting Bitcoin Layer 2s. Trusted providers usually have stronger security measures in place, which means less risk of hacks or fraud.
Use Multi-Sig for Extra Protection
Multi-signature wallets (multi-sig) are a smart way to boost security. They require multiple private keys to approve a transaction, meaning that even if one key is compromised, your funds are safe.
Keep Up with Updates and Vulnerabilities
Stay in the loop by following updates from the Layer 2 project’s team. If there are any vulnerabilities or security patches, you want to be the first to know so you can adjust your setup and protect your assets.
Diversify and Limit Exposure
Don’t go all-in on one Layer 2 solution. Spread your assets across different platforms and wallets to reduce the risk. If something goes wrong with one, you won’t lose everything.
Rubic: Bridging Bitcoin and EVM Chains Securely
Founded in 2020, Rubic Exchange (RBC) plays a key role in the cross-chain ecosystem by connecting Bitcoin with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) chains. Its approach to cross-chain interoperability empowers users and dApps to interact across multiple blockchain environments easily.
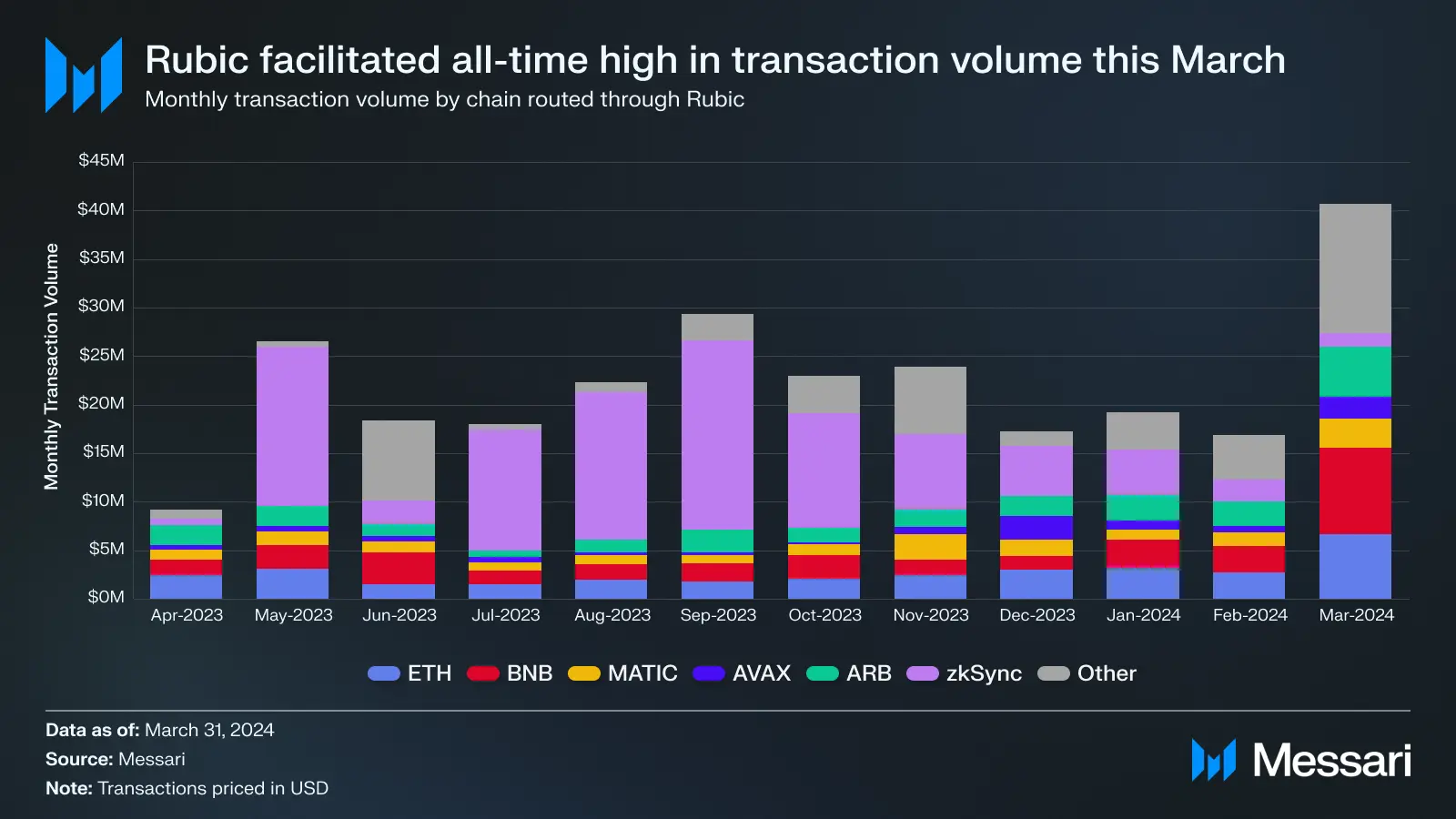
Image source: https://messari.io/report/understanding-rubic
Cross-Chain Functionality
Rubic supports over 80 blockchains and testnets, including EVM and non-EVM networks like Bitcoin, facilitating on-chain and cross-chain crypto swaps for more than 15,500 assets. With integrations spanning 220+ decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and bridges, the platform ensures users get the best rates and liquidity through its Smart Routing technology. This functionality optimizes transaction paths, making trading assets like Bitcoin or EVM-compatible tokens seamless.
Prioritizing Security and Decentralization
Security is a top priority for Rubic, which operates fully decentralized, keeping users’ funds in their wallets during transactions. No KYC is required, preserving user privacy and autonomy. Your funds always stay in your wallet and never on the exchange. Every transaction is conducted via API by sending calls to providers’ smart contracts, reducing the risk of hacks and attacks, such as DDoS.
Innovation and User Experience
Rubic distinguishes itself from other cross-chain aggregators, like LI.FI, XY Finance, and Bungee, by continuously updating its platform to enhance user experience, with features like SwapToEarn and its staking initiatives.
By focusing on emerging chains like Blast, Linea, and Scroll, Rubic positions itself as the central router in the evolving cross-chain ecosystem. As these new chains grow, Rubic can be the go-to platform for seamless asset transfers across different blockchain environments.
Rubic is tackling one of crypto’s biggest challenges: interoperability. With its integrated platform, Rubic bridges the gaps between blockchains, including Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions, making cross-chain transactions simpler and more efficient for users. If you’re looking to interact across Bitcoin Layer 2 networks and other chains, Swap Now and experience the benefits of streamlined cross-chain swaps firsthand.
Future Outlook: Survival of Layer 2 Networks
As institutional interest in BTC shows no sign of abating, Layer 2s could play a starring role in creating a lasting bridge to the traditional finance sector—with interoperability a key focus as these solutions continue to reduce fragmentation among blockchains.
While there is a lot to be bullish about, there are challenges that Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions are still working to overcome.
- Scarcity of Blockspace: Did you know Bitcoin’s blockspace is capped at just 4MB? That might not sound like much, but when you consider the growing demand for Rollups, it’s a real bottleneck that could lead to higher fees and fewer viable projects.
- Economic Viability: For rollups to remain economically viable, they need to generate substantial revenue from transaction fees on their own networks. According to a recently published Galaxy report on Bitcoin data availability, a ZK-Rollup would need to produce between $459,000 and $2.3 million in monthly revenue from L2 transaction fees to cover the costs of posting data to Bitcoin, depending on the fee rates.
- Impact of Competition: The introduction of multiple Bitcoin Layer 2s will intensify competition for blockspace, likely driving up fees for all users, including the networks themselves. This could create a scenario where only a few Layer2s can afford to operate profitably on Bitcoin. Although the added functionalities could increase the value of Bitcoin, market saturation may dilute the focus and impact Bitcoin’s perception as a stable digital currency.
The future of Bitcoin Layer 2s hinges on how well they handle the challenges ahead. As the trade-offs between risk and reward become clearer, we’ll likely see the level of investment and development in these networks fluctuate. It’s also uncertain whether rollups on Bitcoin will really catch on, as they don’t directly compete with the cheap, fast payments that Bitcoiners already rely on through proven Layer 2 solutions. In fact, rollups could follow a path similar to Liquid—low volume and low interest—as many users prefer to simply “stack sats and HODL.”
But to understand where we are today, it’s worth reflecting on how Bitcoin started. Back in the early days, the vision was clear: peer-to-peer payments in a trustless network. That’s what drew so many early adopters—the promise of breaking free from traditional financial systems.
Fast forward to today, and Bitcoin has evolved far beyond those early visions. Consequently, Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions are driving this transformation, addressing scalability issues and expanding Bitcoin’s functionality. Major advancements in technology, user adoption, and even integration with traditional finance present bold opportunities ahead.
The network that once struggled with slow transaction times is now positioning itself as the backbone of a future global financial system. For those who believed in Bitcoin from the start, this evolution feels like the payoff. Layer 2 solutions won’t just keep Bitcoin relevant—they’ll open up new possibilities in a rapidly changing financial landscape. And the best part? We’re still early.
Sources
- https://bitcoinvisuals.com/lightning
- https://sphinx.chat/
- https://blockstream.com/liquid/
- https://eprint.iacr.org/2016/575.pdf
- https://counterparty.io/
- https://www.kucoin.com/learn/crypto/top-bitcoin-layer-2-projects
- https://crypto.com/university/what-are-bitcoin-layer-2s
- https://tangem.com/en/blog/post/bitcoin-layer-2-blockchains/
- https://www.rapidinnovation.io/bitcoin-layer-2-development
- https://www.hiro.so/blog/bitcoin-layer-2s-the-future-of-the-bitcoin-ecosystem
- https://coingape.com/top-bitcoin-layer-2-projects/
- https://alexlab.co/blog/top-bitcoin-layer-2-projects
- https://www.globallegalinsights.com/practice-areas/blockchain-laws-and-regulations/04-layer-2-sequencing-demystified-a-lawyer-s-introduction/
- https://www.bitcoinrollups.io/
- https://bitvm.org/bitvm.pdf
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/digital-assets/2024/06/07/bitcoin-and-the-future-of-the-lightning-network/
- https://lightning.network/lightning-network-summary.pdf
- https://blog.liquid.net/the-truth-about-liquid/
- https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/bitmap-tech
- https://www.gate.io/learn/articles/what-is-merlin-chain-all-you-need-to-know-about-merl/2285
- https://rootstock.io/static/a79b27d4889409602174df4710102056/RS-whitepaper.pdf?_gl=1*khjyo*_gcl_au*MTYxMDYzMDQzMy4xNzI0Njc5MDQ0
- https://blog.rootstock.io/noticia/bitcoin-layer-2-smart-contracts/
- https://docs.stacks.co/stacks-101/bitcoin-connection
- https://messari.io/report/understanding-rubic
- https://www.galaxy.com/insights/research/exploring-bitcoin-for-data-availability/
- https://coinbureau.com/analysis/bitcoin-layer-2/#other-emerging-bitcoin-layer-2-solutions
- https://bitcoinmagazine.com/technical/zk-rollups-are-coming-to-bitcoin-heres-all-you-need-to-know

